Wilberforce
Pendulum

This apparatus
allows to investigate the motion of a peculiar mass-spring
oscillator named Wilberforce Pendulum, where the coupling
between translational and rotational motions is very effective.
A special Non Contact Rotation Sensor and a SONAR, measuring the angular and the vertical displacements respectively, allow a complete characterization of the two coupled oscillators in real time.
A special Non Contact Rotation Sensor and a SONAR, measuring the angular and the vertical displacements respectively, allow a complete characterization of the two coupled oscillators in real time.
Figure 1: the pendulum
- Analysis of various pendulum motions
- Study of beatings
Material included :
- pendulum holder
- spring
- mass
- NCRS rotation sensor
- Sonar
A detailed analysis of recorded data yields plots for the various components of the associated energy vs. time (kinetic and elastic, both for vertical and torsional motions, and the coupling term).
It may be shown how different initial conditions lead to different behaviors (beatings between vibration and rotation or regular exponential decay of both oscillations when one of the two fundamental modes is excited).
FFT analysis reveals the small difference between the frequencies of the two modes.
Beating is shown in Figure 2 : vertical oscillations slowly damp out while rotational oscillation increases; then the process is reversed and the energy exchange between the two modes proceeds.
From measurements of the displacement z and of the rotation angle α we get the time evolution of the traslational energy ET and of the rotational energy ER :
ET= EkT + EeT= (m/2)v2+(k/2)z2
( m mass, v=dz/dt velocity and k elastic constant).
ER= EkR + EeR= 1/2 I ω 2 +(D/2) α2
( I momentum of inertia, ω=dα/dt ' angular velocity and D torsion constant).
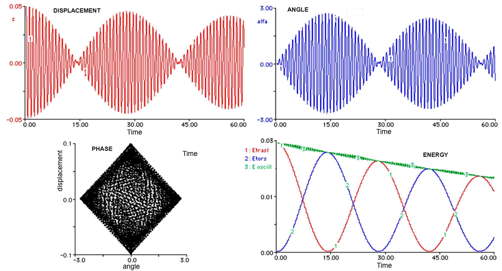
Figure 2. The beating mode
Required material, not included:
A suitable choice of the ratio between initial angle and displacement delete the beating and the energy is half-splitted between rotational and translational components , as shown in Figure 3.
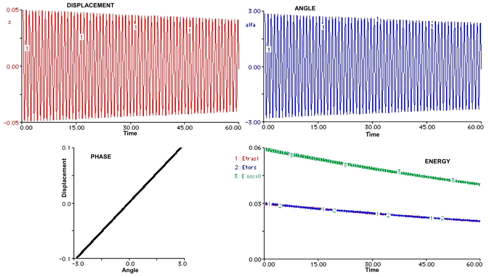
(see: The Wilberforce pendulum: a complete analysis through RTL and modelling ,
Proceeding Int. GIREP Sem. , Udine, 2003)
LabTrek produces two robotized versions of the Wilberforce pendulum : one without sensors (for scientific museums), and one with sensors (for educational laboratories) which allow easy exciting the different modes (beating, and two fundamental modes) by using step motors driven by Arduino (a magnetic actuator stops the pendulum motion when you want to change mode).
Movie showing the 3 oscillation modes in a robotized version
Details of the 3 different modes :
Beating mode
Left fundamental mode
Right fundamental mode